
Once again, they will try to find out if there is life on the Red Planet.
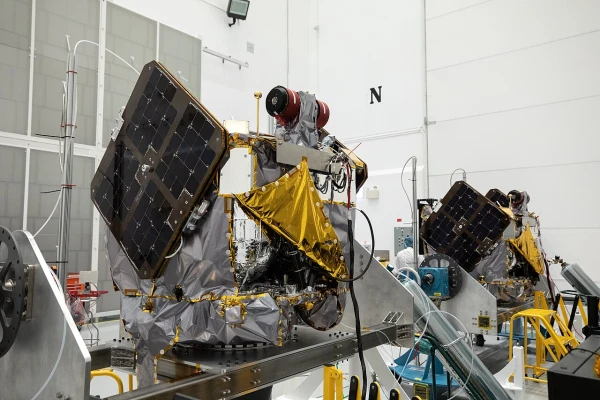
NASA employees have published images that have become the "first light" for the ESCAPADE mission spacecraft — that is, the first pictures taken from space. Just a week after launch, one of the two spacecraft heading to Mars captured these images during the commissioning phase, when engineers check that all systems and instruments are functioning properly.
The images, obtained by the VISIONS cameras onboard the spacecraft, were taken from a distance of 885,240 kilometers from Earth. They show the space along the solar panel of the spacecraft.
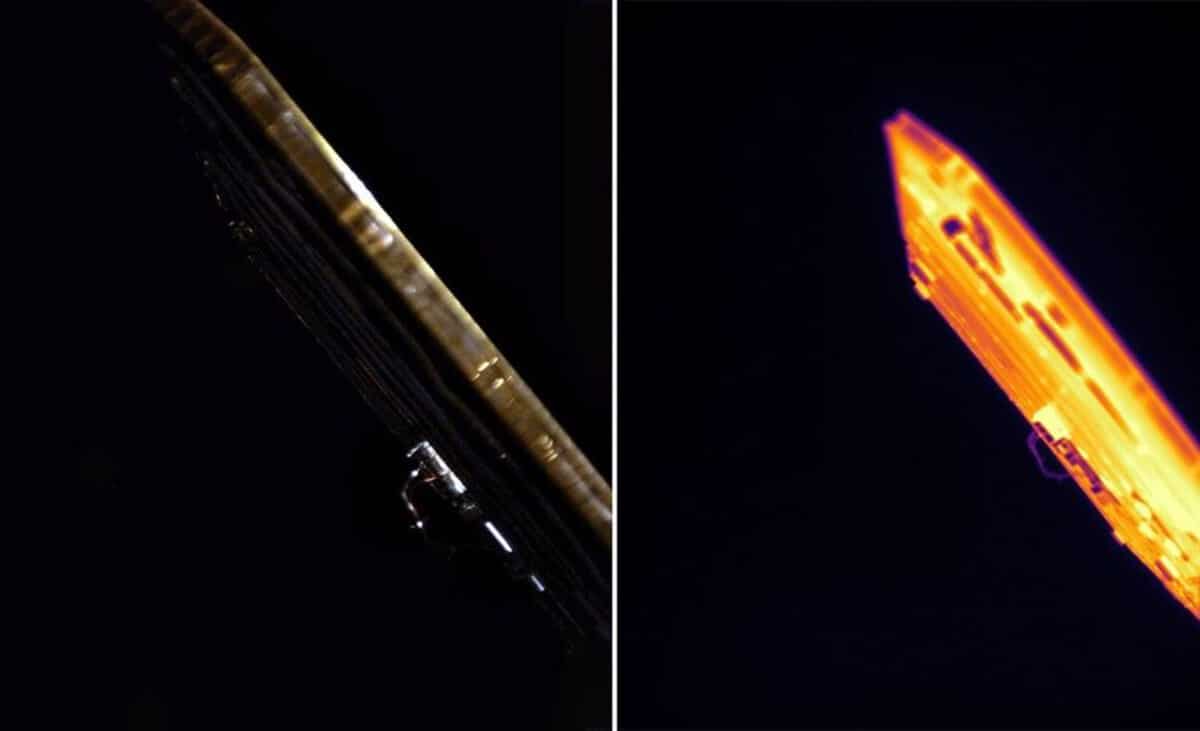
The left image shows a picture captured by the visible light camera. The right one was taken by an infrared sensor, which displays which areas of the solar panel are heated more and which remain cooler.
When the spacecraft reach Mars, the visible light camera will attempt to capture Martian auroras, while the infrared sensor will record temperature changes on the Martian surface at sunrise and sunset.
Both orbiters of the ESCAPADE mission, costing 79 million euros, will study the magnetosphere of the Red Planet and analyze the processes of interaction between energetic particles of the solar wind and the Martian atmosphere.
On June 15, 2021, the American-New Zealand private space company Rocket Lab signed a contract with the California Institute of Technology's Jet Propulsion Laboratory to create two spacecraft, EscaPADE (named Blue and Gold, in honor of the colors of the University of California). Initially, it was planned that both spacecraft would be launched together with the Psyche spacecraft, but the postponement of its launch led to the necessary conditions for orbiting Mars not being met. Instead, the New Glenn rocket was chosen for the launch, making this mission its second launch.
They will spend about a year at the L2 Lagrange point of the system, waiting for a favorable position of Earth and Mars. In November 2026, they will return to Earth to perform a gravity assist maneuver, after which there will be a 10-month flight to Mars, culminating in entering Mars' orbit in September 2027. After that, for 9 months, the spacecraft will be calibrating scientific instruments and achieving the target high-elliptical orbit. Subsequently, they will diverge into different orbital planes, allowing the study of the spatial variability of the processes of interaction between Mars' magnetosphere and the solar wind.














Leave a comment