
The German equipment on the spacecraft has been turned off for almost 4 years.
The detectors of the Russian telescope ART-XC have surprised scientists, as they have inexplicably started to work better rather than worse over the 6 and a half years of operation. This was stated by the scientific supervisor of the ART-XC telescope, Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences Alexander Lutovinov, during the conference "High Energy Astrophysics Today and Tomorrow 2025" (HEA-2025) at the Space Research Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
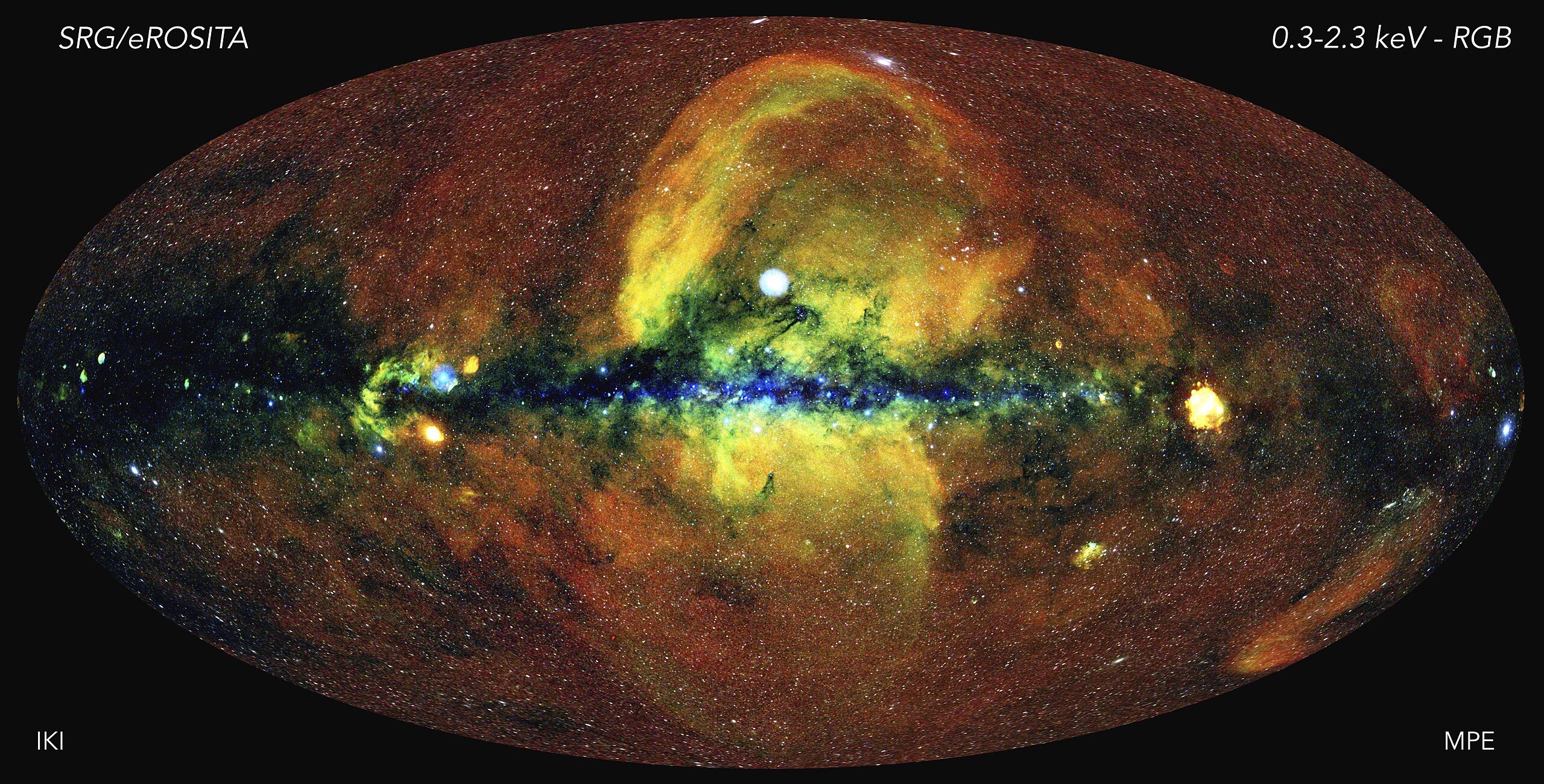
The "Spectrum-Röntgen-Gamma" ("Spectrum-RG" or SRG) observatory was launched into orbit on July 13, 2019. It consists of two telescopes — the German eRosita, operating in the soft X-ray range, and the Russian ART-XC, operating in the hard X-ray range. On February 26, 2022, after the start of the military operation in Ukraine, the German side requested NPO Lavochkin to switch the eRosita telescope to a safe mode, in which it remains to this day.
The Russian telescope ART-XC, as part of the space observatory, consists of seven mirror systems. In the focal plane of each of them is a position-sensitive and spectrometric semiconductor X-ray detector based on cadmium telluride, developed and created at the Space Research Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
The first all-sky survey by the eROSITA telescope in soft X-ray radiation was completed on June 11, 2020, based on its data, 1.1 million X-ray sources were cataloged, mainly active galactic nuclei (77%), stars with strong magnetically active hot coronae (20%), and galaxy clusters (2%), X-ray binary stars, supernova remnants, extended star formation regions, as well as transient processes such as gamma-ray bursts.

"The detectors work every day; we only pause for 15 minutes to perform some depolarization because a certain polarization effect accumulates over the day, which worsens the resolution. The detectors are doing great. There is a concept of leakage current, which should increase with rising radiation load and degradation, but for some reason, it is decreasing in our case," Lutovinov said. "So the detectors are getting better and better, despite being in space. I don’t know why."
At the end of 2017, the cost of just creating the eROSITA telescope was estimated at €100 million. "Spectrum-RG" is one of the best X-ray observatories for the next 10–15 years (the launch of the European ATHENA will not occur before 2031). Unlike previous X-ray space telescopes, which have very limited fields of view, "Spectrum-RG" is capable of making a complete survey of the sky with record sensitivity.










Leave a comment