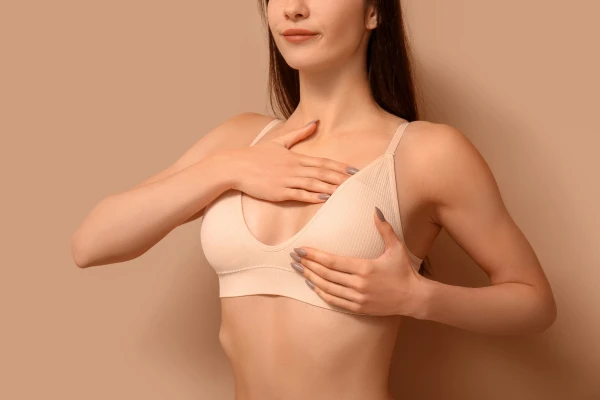

Breast augmentation is one of the most sought-after procedures in aesthetic medicine. In the USA, it is chosen annually by tens of thousands of women, and a similar trend is observed in European clinics, including areas where plastic surgery in Riga is developing.
Demand is explained by a stable safety protocol and predictability of results.
Age Restrictions
The procedure is technically possible at any age, but the legislation of most countries, including Latvia, allows breast augmentation only after reaching 18 years of age. The purpose of this restriction is to exclude interventions before the natural formation of tissues is complete.
Safety of Implants
Modern implants undergo multi-stage testing. They maintain integrity under standard loads and do not interact with surrounding tissues. Placement under the pectoral muscle minimizes contact with the breast tissue. There is no impact on hormonal processes, the ability to conceive, or breastfeeding. Myths about household ruptures or "leaks" of contents are not supported by clinical data.
Complexity of the Operation
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia. The surgeon makes a small incision, forms a pocket, and places the implant. After suturing, the patient spends about a day in the hospital. Afterward, a return to basic activities is allowed while avoiding strain on the upper shoulder girdle. Full adaptation of the implant takes several weeks.
Choosing Size and Shape
The optimal volume is determined by initial proportions, tissue condition, and the thickness of soft structures. The shape of the implant - round or anatomical - is selected based on the specific type of chest. The goal is to achieve a stable contour without excessive skin tension.
Risks and Limitations
Standard risks include infection, capsular contracture, and temporary loss of sensitivity. Prevention includes antibiotic protection, correct implant placement, and adherence to recovery protocols. Limitations concern training, heavy lifting, and sudden arm movements until healing is complete.
Post-Operative Monitoring
Follow-up visits allow for assessing the position of the implants, the condition of scars, and tissue tone. Further monitoring is required once a year to exclude late complications. The EU has standards regulating long-term monitoring of patients after aesthetic interventions.
As a form of advertising












Leave a comment