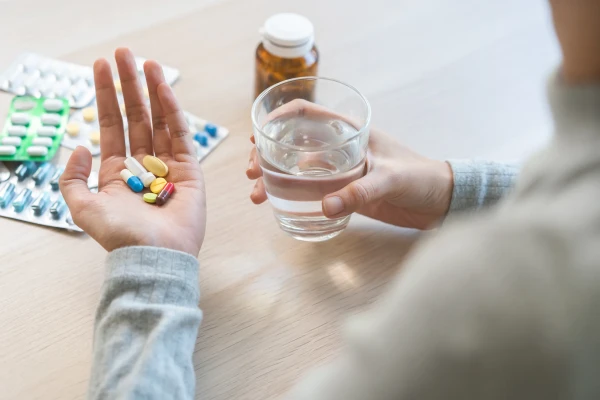

Antibiotics have long been perceived as "the strongest medicine." At the first signs of a cold, flu, or ARVI, many automatically reach for them, hoping to recover faster. However, in practice, it is more complicated: antibiotics are serious medications, and their benefits do not always outweigh the potential harm.
What Are Antibiotics and What Are Their Benefits
Antibiotics are drugs with pronounced antibacterial action, developed in the 20th century. They have saved millions of lives by making many deadly diseases treatable.
By origin, antibiotics can be natural (from plants, animals, or microbes), semi-synthetic, and synthetic. Based on their mechanism of action, they are divided into two groups: some directly kill bacteria, while others inhibit their reproduction, allowing the immune system to cope with the infection.
The first antibiotic was penicillin from mold fungi. It had a narrow spectrum of action and practically did not affect the beneficial microflora, so its harm was minimal.
Why Antibiotics Can Be Dangerous
Modern antibiotics are often broad-spectrum, meaning they affect many types of bacteria simultaneously. This leads to the destruction of the beneficial gut microflora, dysbiosis, decreased immunity, and increased vulnerability to new infections.
A particular problem is the development of bacterial resistance. Many microorganisms adapt to the drugs, and an antibiotic that was previously effective may become ineffective. Sometimes, it is necessary to change the treatment regimen several times to achieve results.
Antibiotics also place a burden on the liver, kidneys, and gallbladder. Allergic reactions are possible, ranging from skin rashes to severe conditions such as angioedema.
Special caution should be exercised during pregnancy and breastfeeding: many drugs can disrupt fetal development and affect the child's immune system.
Some antibiotics affect the nervous system, causing dizziness, weakness, and coordination disorders.
Conclusion
Antibiotics are not a universal remedy and not a "magic pill." They save lives when used appropriately, but improper and uncontrolled use can cause serious harm. They should only be taken as prescribed by a doctor, following the dosage and course.
A conscious approach to treatment is the best way to maintain health and avoid dangerous consequences.













Leave a comment