The high-altitude region is softening its nature.
The second Chinese scientific expedition to the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau has yielded significant practical results. As reported by the Xinhua News Agency, the participants of the expedition shared the main outcomes in Lhasa, the capital of the Tibet Autonomous Region (Southwest China).
The head of the expedition, academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences Yao Tandong, stated that the main achievements concern such crucial aspects as environmental protection, disaster prevention, natural resource exploration, carbon emission accounting, road safety, and development of border areas.
According to him, the focus is primarily on the scientific justification of legislation for ecological protection on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, the creation of a platform for Earth observation, as well as innovative technologies for disaster prevention and response in the permafrost region to benefit large infrastructure projects.
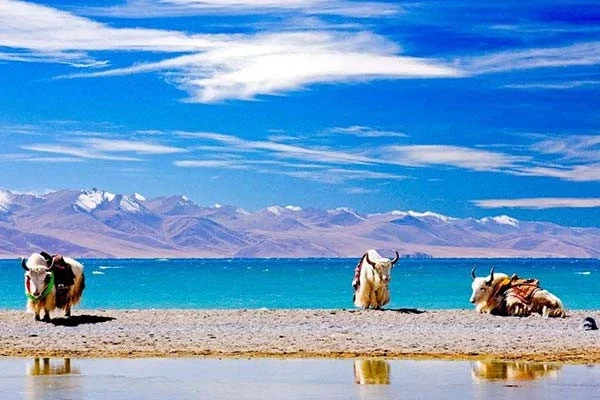
The scientist noted that currently, there are trends of climate warming, soil moisture increase, and "greening" on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. This, according to the academician, contributes to the intensification of climate change impacts at both regional and global levels.
It was also established that the water supply potential of this "water tower of Asia" has significantly increased: by the end of this century, an increase in runoff volume of nearly half is expected.
The second scientific expedition to the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau began in August 2017 and covered its entire territory. To date, more than 30,000 specialists from three thousand research groups have been involved in the comprehensive studies.